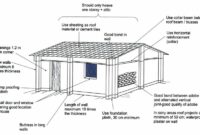
Materials for earthquake resistant – The Philippines, situated along the Pacific Ring of Fire, is highly prone to earthquakes.
Given this, constructing earthquake-resistant homes is essential to ensure safety and reduce potential damage during seismic events.
Choosing the right materials plays a critical role in designing homes that can withstand the forces of nature.
Here’s a comprehensive look at the best materials for building earthquake-resistant houses in the Philippines.
1. Reinforced Concrete
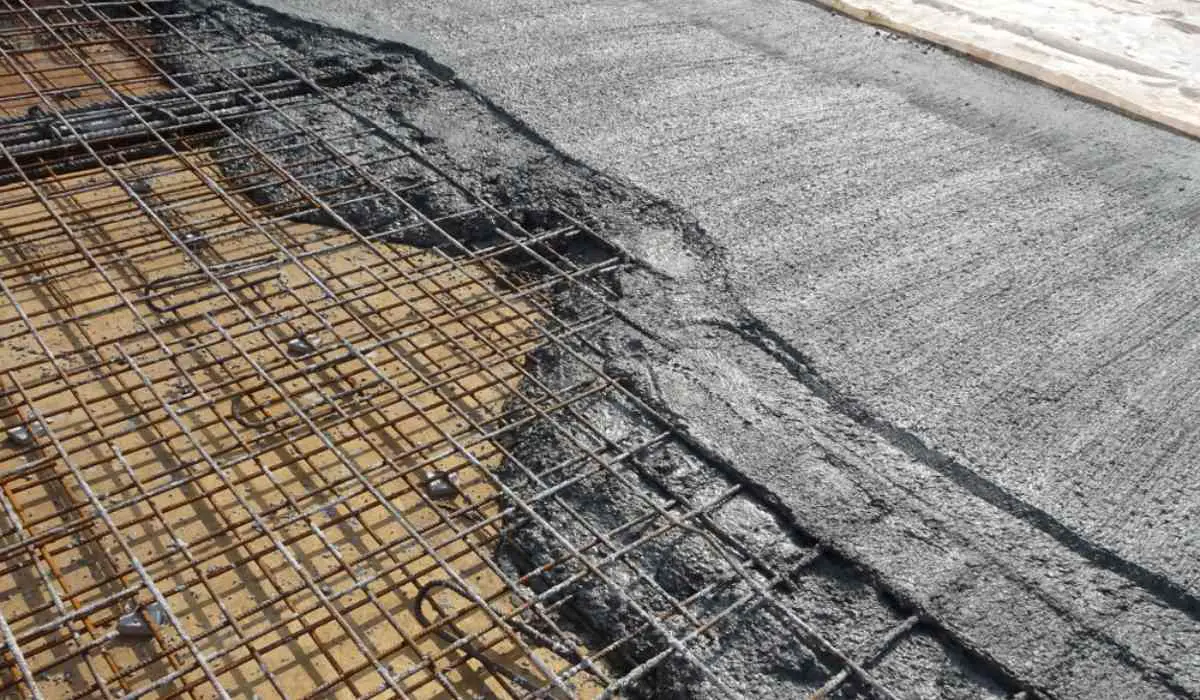

Reinforced concrete is one of the most reliable and widely used materials for earthquake-resistant structures.
By combining concrete with steel reinforcement bars (rebar), the material gains both tensile strength (from steel) and compressive strength (from concrete).
This makes it durable and capable of absorbing and dispersing seismic energy during an earthquake.
- Why It’s Effective: Reinforced concrete can withstand both tension and compression, which are the primary forces experienced during an earthquake. Properly designed concrete structures with flexible joints can sway without breaking.
- Considerations: Ensure that the concrete mix is of high quality, and proper placement and curing of the material are followed during construction. Poorly made concrete can crack under stress.
read also: Staple Foods to Prepare When a Storm Disaster Is Approaching
2. Steel Frames
Steel is known for its flexibility and high strength-to-weight ratio, making it an excellent material for earthquake-resistant homes.
Steel frames are capable of bending and absorbing energy without collapsing, allowing structures to move with the seismic forces instead of resisting them rigidly.
- Why It’s Effective: The ductility of steel allows buildings to deform without failing. This property ensures that the structure remains intact even under intense shaking, which is essential during a large earthquake.
- Considerations: Steel is relatively more expensive than other materials, but its long-term benefits in terms of durability and earthquake resistance often justify the cost.
3. Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT)
Cross-laminated timber is an innovative and sustainable material that has been gaining popularity in earthquake-prone regions worldwide.
CLT panels are made by gluing layers of wood together at perpendicular angles, which creates a strong and flexible building material.
- Why It’s Effective: CLT structures are lightweight and can flex during an earthquake, reducing the amount of stress placed on the building. Timber is also a renewable resource, making it environmentally friendly.
- Considerations: CLT is still relatively new in the Philippines, but it has shown promise in seismic tests around the world. Builders should ensure proper design and construction to maximize earthquake resistance.
4. Bamboo
Bamboo is a traditional and abundant material in the Philippines, and when used correctly, it can be highly effective in earthquake-resistant construction.
Bamboo’s flexibility and strength make it an ideal material for homes in rural or low-income areas prone to seismic activity.
- Why It’s Effective: Bamboo is highly resilient and flexible, which allows it to bend without breaking during an earthquake. It is also lightweight, reducing the overall load on the structure.
- Considerations: Bamboo must be treated to prevent insect infestations and decay. When combined with modern building techniques, bamboo can be used to create low-cost, earthquake-resistant homes.
5. Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC)
Autoclaved aerated concrete is a lightweight, precast building material that has become popular in earthquake-resistant construction due to its combination of strength and low density.
AAC blocks are easy to install and offer excellent thermal insulation as an added benefit.
- Why It’s Effective: The material’s lightweight nature reduces the seismic forces acting on the building, while its compressive strength ensures structural integrity. AAC blocks can also be reinforced with steel bars for added stability.
- Considerations: AAC blocks require careful handling during construction to prevent damage, and proper reinforcement should be added for increased earthquake resistance.
6. Rubber Bearings (Seismic Isolators)
While not a building material in the traditional sense, rubber bearings (or seismic isolators) are vital components in earthquake-resistant construction.
These devices are placed between a building’s foundation and superstructure to isolate the building from ground movement during an earthquake.
- Why It’s Effective: Seismic isolators absorb the shock of an earthquake and prevent it from transferring directly to the building. This technology allows the building to remain steady even during strong tremors.
- Considerations: Seismic isolators are an advanced construction technology that can be costly, but they offer unmatched protection for buildings in earthquake-prone regions.
7. Fiber-Reinforced Polymer (FRP)
Fiber-reinforced polymer is a composite material made from a polymer matrix reinforced with fibers (usually glass, carbon, or aramid).
It is increasingly being used in earthquake-resistant construction because of its high strength, lightweight properties, and resistance to corrosion.
- Why It’s Effective: FRP can be wrapped around columns and beams to provide additional reinforcement without adding significant weight to the structure. This helps the building maintain its integrity during seismic events.
- Considerations: FRP is a relatively expensive material and may not be necessary for all residential buildings, but it is highly effective for reinforcing critical structural elements.
8. Engineered Wood Products
Engineered wood products, such as plywood and laminated veneer lumber (LVL), offer better performance than traditional wood when it comes to earthquake resistance.
These products are designed to have consistent strength and stability, making them suitable for load-bearing walls and floors in seismic areas.
- Why It’s Effective: Engineered wood is less prone to warping and splitting compared to solid wood, which makes it more reliable during an earthquake. The flexibility of wood allows buildings to absorb seismic forces without cracking or collapsing.
- Considerations: Proper installation and bracing are essential to ensure the best earthquake resistance.
9. Earthquake-Resistant Glass
While glass is generally a fragile material, modern technology has developed earthquake-resistant glass that can withstand seismic activity.
This type of glass is often laminated or tempered to prevent it from shattering during an earthquake.
- Why It’s Effective: Earthquake-resistant glass remains intact even when subjected to heavy vibrations, reducing the risk of injury and property damage caused by broken glass.
- Considerations: This type of glass is more expensive than regular glass, but it’s a worthwhile investment in earthquake-prone areas.
Conclusion
materials for earthquake resistant – Building earthquake-resistant homes in the Philippines is crucial for ensuring the safety of occupants and protecting property from seismic damage.
Reinforced concrete, steel frames, bamboo, and modern materials like CLT and AAC blocks offer the necessary flexibility, strength, and durability to withstand earthquakes.
Additionally, advanced technologies such as seismic isolators and earthquake-resistant glass can further enhance the structural resilience of homes.
When constructing an earthquake-resistant house, it’s important to consult with engineers and architects who specialize in seismic design to ensure that the building meets safety standards and is equipped to handle the forces of nature.
By using the right materials and techniques, homeowners in the Philippines can build safer, more resilient homes for the future.